PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
924-88-9
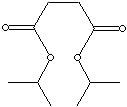
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
-40 C
0.983
APPLICATIONS
Succinic Acid (also called Butanedioic Acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with four carbon atoms, occurring naturally plant and animal tissues and that plays a significant role in intermediary metabolism (Krebs cycle). It is a colourless crystalline solid with a melting point of 185-187º C, soluble in water, slightly dissolved in ethanol, ether, acetone and glycerine, but not dissolved in benzene, carbon sulfide, carbon tetrachloride and oil ether. The common method of synthesis of succinic acid is the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic acid or its anhydride. Succinic acid has uses in certain drug compounds, in agricultural and food production, and in perfume esters manufacturing.
There are almost infinite esters obtained from thousands of potential starting materials. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol, e.g., carboxylic acid esters, phosphoric acid esters, and sulfonic acid esters. Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application selections.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
ACIDITY
MOISTURE
0.05% max
ORGANIC IMPURITY
1.0% max
COLOR
- Plasticizer for polymers
- Biodegradable solvents and lubricants
- Engineering plastics
- Epoxy curing agent
- Adhesive and powder coating
- Corrosion inhibitor
- Perfumery and pharmaceutical
- Electrolyte
|
Structure & Length |
Common Name |
Formula |
Melting Point |
|
Straight C2 |
Oxalic Acid (Ethanedioic Acid) |
HOOCCOOH |
187 C |
|
Straight C3 |
Malonic Acid (Propanedioic Acid) |
HOOCCH2COOH |
136 C |
|
Straight C4 |
Succinic Acid (Butanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)2COOH |
190 C |
|
Straight C5 |
Glutaric Acid (Pentanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)3COOH |
99 C |
|
Straight C6 |
Adipic Acid (Hexanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)4COOH |
152 C |
|
Straight C7 |
Pimelic Acid (Heptanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)5COOH |
106 C |
|
Straight C8 |
Suberic Acid (Octanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)6COOH |
143 C |
|
Straight C9 |
Azelaic Acid (Nonanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)7COOH |
106 C |
|
Straight C10 |
Sebacic Acid (Decanedioic Acid) |
HOOC(CH2)8COOH |
134 C |